Table of Contents
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a normal chromosomal degenerative disorder caused by the cystic fibrosis penetrating conduct dance regulator (CFTR) gene mutation. CF is a state of life restrictions that are mainly involved in multilateral involvement in respiratory, liver, and gastrointestinal diseases and out -of -pulmonary symptoms. In 2020, there were 1,466 CF care in Ireland.
In recent years, the survival rate of CF has been significantly improved with the median survival period born between 2016 and 2020. This reflects the intensive treatment and a better understanding of the management of multiple symptoms. Very effective modulator therapy (IVACAFTOR and ELEXACACAFTOR-TEZACAFTOR-IVACAFTOR, etc.) will lead to improvement of CF people and improve the removal of CFs from the portable list. I did it.
However, the increase in the complexity of care for old CF groups may provide new tasks such as renal failure, drug -resistant creatures, or latter -lined diseases, which may affect transplantation. There is.
For patients with advanced pulmonary disease, pulmonary transplant remains an important treatment option that has the potential to improve the quality of life and extend the average life expectancy. According to the International Cardiac Transplant Association (ISHLT), the CF represents the third most common adaptation.
Advanced CF pulmonary disease is an important indicator of transplant referral into consideration, and is defined as a forced exhalation amount in 1 second (FEV1) of the forecast value of less than 40 %. Other criteria that may encourage referrals for transplant evaluation include hyperchanicated gas (PCO)2 > 6.6kpa For arterial blood gas tests), ICU hospitalization for respiratory failure, oxygen requirements on the date and time, pulmonary hypertension (pulmonary arterial contraction phase pressure> 50 mmHg) or 6 minutes walk test (6MWT) (6MWT) (6MWT) CF -related diabetes, rapidly decreasing FEV1, motor oxygen requirements, and the number of deterioration of the lungs are an important partial factor in identifying patients who may deteriorate more quickly.
Currently, it is estimated that the median of the survival period after pulmonary transplantation is 6.7 years on average. The survival of the pulmonary transplant that occurs in the CF is related to the median of the 9 -year survival, increasing in 12 years of surviving the first year. Lung transplant is a procedure to extend the life, taking serious risk, all cases are unique and individual. The appropriate patient's early introduction and identification are important for the early optimization of co -diseases, giving the patient deal with modified barriers and minimize postoperative complications.
Portrait
CF is a multiolgan disease, and optimization of coalition diseases is essential in introducing transplantation. Factors, such as extreme body mass index (BMI), control defective diabetes, renal dysfunction, and esophageal motor disorders, are associated with the occurrence of complications after transplantation and poor rehabilitation. It is necessary to consider compliance, misuse of substances, and other psychological social factors.
The rate of gastric floating (GORD) increases significantly during the transplant period, and untreated diseases contribute to pulmonary infection and deterioration of pulmonary function. CF (PWCF) people are prior to Gord, and 55 % of Irish adult CF patients report serious symptoms. Optimization of medical management and the study of surgical intervention must be dealt with early to reduce postoperative symptoms.
Low BMI is an independent danger factor in PWCF mortality. BMIs under the age of 18 are related to the high risk of death in the first year after transplantation. This alone should not delay the introduction of the transplant, but you need to deal with nutritional optimization before the formal evaluation.
CF treatment is complicated and has a heavy burden over a long period of time. Insufficient treatment is related to improving the rate of exacerbation. The prescribed drugs seem to be better than physiotherapy registers and nutritional foods. Evidence that compliance in the pre -transplant environment is inadequate, as a sign that may be insufficient to comply with the transplant environment, as a sign that is considered in pulmonary social factors and the detailed test of the pulmonary transplant. It will not be blurred.
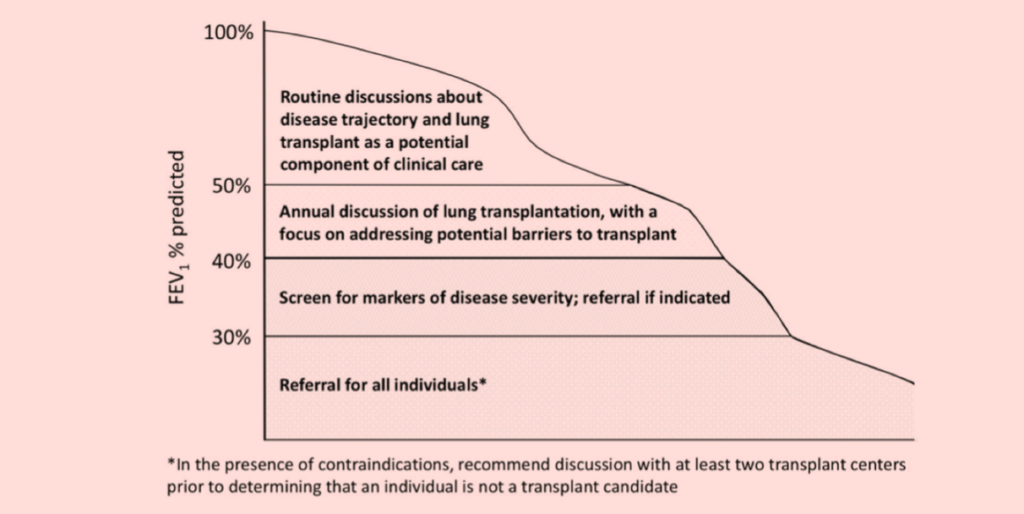
Consensus guidelines for identifying patients who benefit from pulmonary transplant considerations were announced in 2019 by the Cystic Fiscal Foundation. The goal of this document was to support the results of success in order to identify the potential barriers that are transplanted earlier than the conventional referral models. 。 In order to avoid the need for emergency transplantation, we recommend early introduction of appropriate patients ()Figure 1) In order to strengthen the referral process, we focus on early communication between patients and their families.
During the surgery
Double pulmonary transplant is recommended in PWCF because of the risk of mutual pollution and infection related to a single pulmonary transplant. Colony formation of chronic bacteria and multi -agent -resistant organisms are common in CF and bring complicated antibacterial management at the end of the end. When devising an appropriate target antibacterial regimen, it is necessary to consider under surgical specimens and previous culture in addition to local comparison of under surgical antibiotics. We recommend three months of screening of bacteria, fungi, and Mycobacteria pathogens for people with CF in the active transplant list.
infection Burkholderia cenocepacia Complex (BCC) or MyCobacterium Abscessus Increasing the risk of mortality after transplantation is considered a contraindications for transplantation.
The percentage of pneumothorax in CF is 0.64 %, and when pulmonary disease is advanced, the aging rate is more common. Although it is not a clear contraindicated contraindicated for transplantation, it is necessary to give special consideration to these patients during surgery. Those who have received previous chest treatments such as thymus have an increase in the risk of bleeding, but there is no evidence of an increase in mortality.
In some centers around the world, ECMO (extracorporeal oxygen) is used as a transplant bridge. ECMO is related to an increase in complications and can only be used at a specialty center.
In recent years, survival rate
CF was greatly improved in A
The median of the born people predicted surviving survival
50 years between 2016 and 2020
Postoperative
The foundation of cystic fibrosis emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary CF care to ensure the tracking and treatment of CF out -of -pulmonary complications within 6 months to 12 months of pulmonary transplantation. 。 。 Expert evaluation and endoscopic surgery are beneficial for patients with symptoms. It has been shown that there is some relationship between the pre -transplantation sinus culture and the bronchial flush culture after transplantation, suggesting that the sinuses remain the reservoir of the same species after transplantation. Masu. Prevention of antibiotics and airway clearance technology are important to take into account the transplant. Since DN-ASE evidence is insufficient, it is necessary to consider the airway clearance after transplantation, individual decisions on management, and the continuation of inhaled antibiotics.
Liver enzymes need to be monitored at least every year using imaging as needed, and pay attention to the addition of drug liver poisoning after transplantation. Changes in pharmacokinetics need to increase the vigilance when monitoring the CF group's immunosuppressive level.
OGTT's diabetes screening must occur three months to six months after transplantation, except for existing CF -related diabetes.
Considering the risk of osteoporosis and CF -related bone mineral density, it is necessary to schedule DXA scanning six months to 12 months after transplantation.
Renal dysfunction may have pre -transplanted transplantation in CF, and is often multifacinator (diabetes, aminoglycoside, renal stone disease, infectious disease). An abnormal renal function is common in CF pulmonary recipients, and requires a detailed monitoring of an immunosuppressive level and introduction to the kidneys. In two years, 35 % of CF pulmonary transplantation recipients suffer from renal dysfunction after transplantation.
Pregnancy is not recommended for the first two years after transplanting, as acute, chronic rejection and death increase. After two years, it is suitable for small subgroups in patients and there is a serious risk.
Compared to the general group, the overall risk of cancer is increased after 10 times the transplant in non -CF recipients and CF pulmonary recipients 10 times. The risk of colorectal cancer increases 25 to 30 times with CF pulmonary recipients compared to the general group. Everyone with CF and reproduction should occur 3 to 3 at the age of 40. 5 years according to the first result.
Nutritional input after transplantation is required to ensure the appropriate level of lip -soluble vitamins, BMI optimization, and blood sugar control.
Conclusion/Future
Lung transplantation recipients with CF require complicated care that passes many specialized fields. A special clinic with an expert input is important for dealing with both the requirements after transplantation, but also responds to its own CF -related diseases that continue to contribute greatly to the affection rate after the patient's incidence. I am doing it.
At the same time, multiolgan transplantation (lungs, liver, lungs, pancreas, pancreatic pancreas) or step -by -step (lungs, liver, pancreas, kidneys, kidneys) are performed. Simultaneous transplantation safety includes surgery, expertise, and waiting time in multiol gun -assigned context.
The introduction of the CFTR modulator brought a revolution to care at CF. The initial exam that evaluates the effectiveness of these modulators in the CF group excludes patients with advanced pulmonary disease. However, clinical experience has postponed the list of transplantation as a result of positive modulator treatment. Large -scale studies have not yet been conducted to examine the effects of CFTR modulator for out -of -pulmonary symptoms in the environment after transplant, but recent studies have 94 patients after lung transplantation. -The 94 patients who prescribed the tezakaffe agent Ibacoft have reported. The improvement of HBA1C and anemia was observed and did not affect BMI. The rising liver enzyme was only 3 %, but 42 % stopped treatment due to side effects and lack of profits.
Pulmonary transplant can improve the survival and quality of people with the CF and lung disease. With the progress of the CF modulator and improving results, early discussions and introductions are more important in setting a potentially complex population. Early introduction and discussion of transplanting allows you to overcome potential barriers to transplantation and secure the optimal timing and results by transplantation.
See according to the request